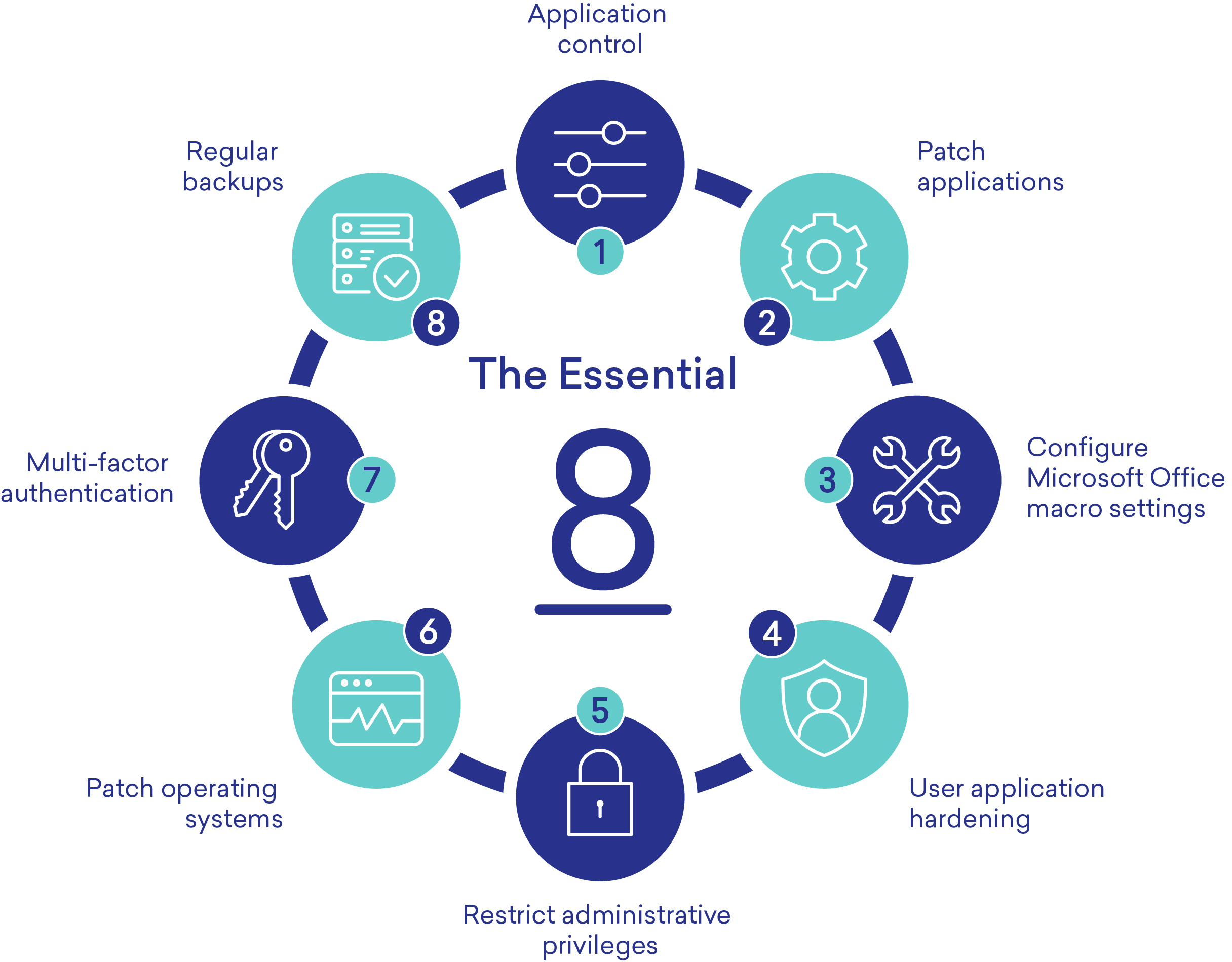
1. Application Control and whitelisting
It’s a no brainer but managing all executables, scripts, HTML applications, installers on any workstation is a good place to start. Preventing any unauthorized pieces of software can stop malware in its tracks from the start.
What is the solution?
Start with a list of whitelisted applications and work from there. Begin by checking each software and the latest versions. Most will have unsupported versions, and some will be unpatched if you haven’t done a check in a while. Take your time to investigate whether the latest versions are stable. In some cases, it’s a good idea to keep up to date with the news from vendors not to miss anything important.
2. Patching applications
Probably something every IT team is familiar with and can do with ease. But the amount of unknown software and SaaS products that each department uses can really put your team into a spin. Over time, unpatched applications can lead to some serious gaps in your security, creating loopholes with each new feature that is added to the application.
What is the solution?
Similarly, to application control and whitelisting, start with the list of whitelisted applications and work from there. Begin by checking each software and the latest versions. Most will have unsupported versions, and some will be unpatched if you haven’t done a check in a while. Take your time to investigate whether the latest versions are stable. In some cases, it’s a good idea to keep up to date with the news from vendors not to miss anything important.
3. Configure Microsoft Office Macro Settings
Macros serve an important purpose in automating and preforming pre-defined tasks for employees in your business. Macros unfortunately can house some nasty surprises with several loopholes and even viruses which can be executed.
What is the solution?
Disabling all macros just won’t cut it! Choosing which macros can be trusted and which can be tricky but not impossible. Digitally signing macro’s is a way to set parameters around trusted and untrusted macros. Using third party trusted certificate authority is crucial and a time effective moving forward. You may need to seek assistance in building out digital signing for the business.
4. User Application hardening
Cherry pick the applications you deem mission critical to the business and do away with everything else. Many of these applications can be used maliciously and in the wrong hands can have significant impacts on your infrastructure and business operations.
What is the solution?
Once these applications are realised, take the time to secure these even further. By default, most of these apps will be installed with the out of the box access permissions and services. Take the time to work out who needs access to the application and what they need access to within the application. Review these often or after any significant updates or changes. Any default passwords should be addressed right away along with closing any unnecessary networking ports for the application.
5. Restrict administrative privileges
Most systems and applications have administrative tools and privileges you can use to exclude and restrict a number of permissions. Users with elevated access to your platforms, devices, workstations and software can be a potential risk if left unchecked.
What is the solution?
Similar to the pervious elements in the essential 8, take note of your list of whitelisted applications, who has what privileges and who has administrative access. Continue to move onto the workstations any networking devices, IoT devices and firewalls. Be sure to deactivate any employees that have left the business or employees that have changed roles.
6. Patching operating systems
Patching operating systems is similar to patching application in that critical updates for the system close any security loops or vulnerabilities. Regardless of the operating systems you use, they need to be patched!
What is the solution?
Setting a time every week to check for patches and updates is a good place to start. Explore how patches are generally acquired from the vendors, how they are tested and deployed. Look for ways to streamline this process and always keep up with the patching schedule you put in place.
7. Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) adds that extra layer of protection for your users, with the popularity of mobile devices it’s easy to put a new solution in place. MFA builds on your existing username and password strategy and has the potential to transform the way your teams access your systems and applications.
What is the solution?
There are a growing number of MFA solutions in the marketing, from Microsoft to Google, Cisco and beyond. It’s about finding the right fit for your organisation because MFA is no simple feat to implement. MFA solutions take time, effort, deep thought and money, chat with the stakeholders of the business and ask them “could we be more secure?” And is MFA the solution.
8. Regular backups
Daily backups are quite common in most businesses and has been that fail safe needed for any server and storage issues where data might have been lost.
What is the solution?
Again there are heaps of products and services in the market tailored to suit any business requirement. It is critical to review your current backup solutions and process and sure up any gaps you find. A good rule to follow is the 3-2-1 rule.
3 – Do you keep at least three copies of your data?
2- Do you store the data in at least two different formats? (Disk, tape)
1- Do you keep 1 copy offsite? Online or offline?
Read more on the 3-2-1 rule here.





